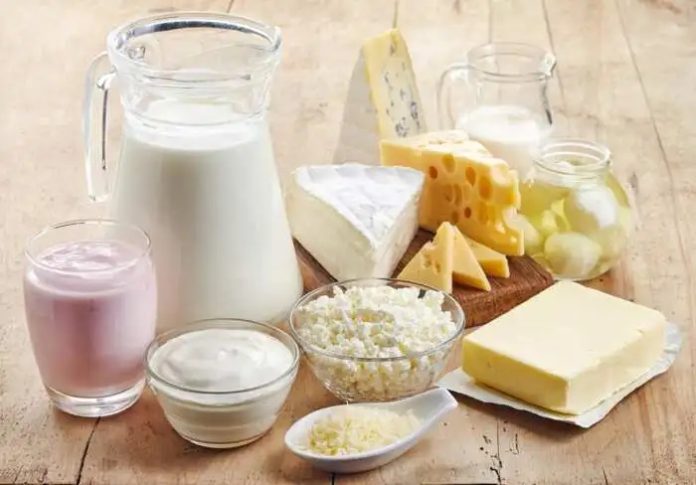
Camel milk is a unique and nutritious option that’s high in protein, calcium, potassium, and iron. With its distinctive sweet and nutty taste, it’s a viable alternative for those who struggle with lactose intolerance or have allergies to cow’s milk. In parts of Africa and Asia where camels are key to the economy, camel milk products are common dietary staples. They’re also gaining traction in Western countries due to their health benefits.
You can find camel milk in various forms including fresh, powdered, or frozen, and it can be consumed on its own or incorporated into foods like yogurt, cheese, and ice cream.
Reasons to Include Camel Milk in Your Daily Diet
Rich in Nutrients: Camel milk is packed with vital minerals and vitamins such as protein, calcium, potassium, and iron.
Low Fat and Lactose Content: Ideal for those who are lactose intolerant or allergic to cow’s milk, camel milk has reduced levels of fat and lactose.
Boosts Immune Function: High in antibodies, camel milk can be beneficial for those with weaker immune systems.
Potential Diabetes Treatment: Camel milk contains insulin-like peptides that show promise in diabetes management.
Improves Skin Health: Rich in skin-nourishing nutrients like vitamin C and zinc, camel milk can help promote healthy skin.
Heart-Healthy: High potassium levels in camel milk contribute to blood pressure regulation and heart protection.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Consuming camel milk may reduce bodily inflammation.
Versatile Supplement: While it’s a great dietary addition for most people, those who have difficulty consuming other foods may find it particularly beneficial.
Who Should Avoid Camel Milk?
Lactose Intolerant Individuals: Though camel milk has less lactose, it may still pose issues for some people who are lactose intolerant.
Those Allergic to Cow’s Milk: The similarity between cow’s milk and camel milk may trigger allergies.
Weakened Immune Systems: Unpasteurized camel milk could contain harmful microbes and is not recommended for those with compromised immunity.
Pregnant and Nursing Women: Due to limited research on its safety, pregnant and breastfeeding women are advised to avoid camel milk.
Salt-Sensitive Individuals: Some camel milk products may be high in salt, which could be a concern for those watching their salt intake.
People on Blood Thinners: The vitamin K in camel milk can interfere with blood-thinning medications. Consult your doctor before incorporating camel milk into your diet.
If you’re considering adding camel milk to your diet, it’s best to purchase from reputable suppliers like Desert Farms.